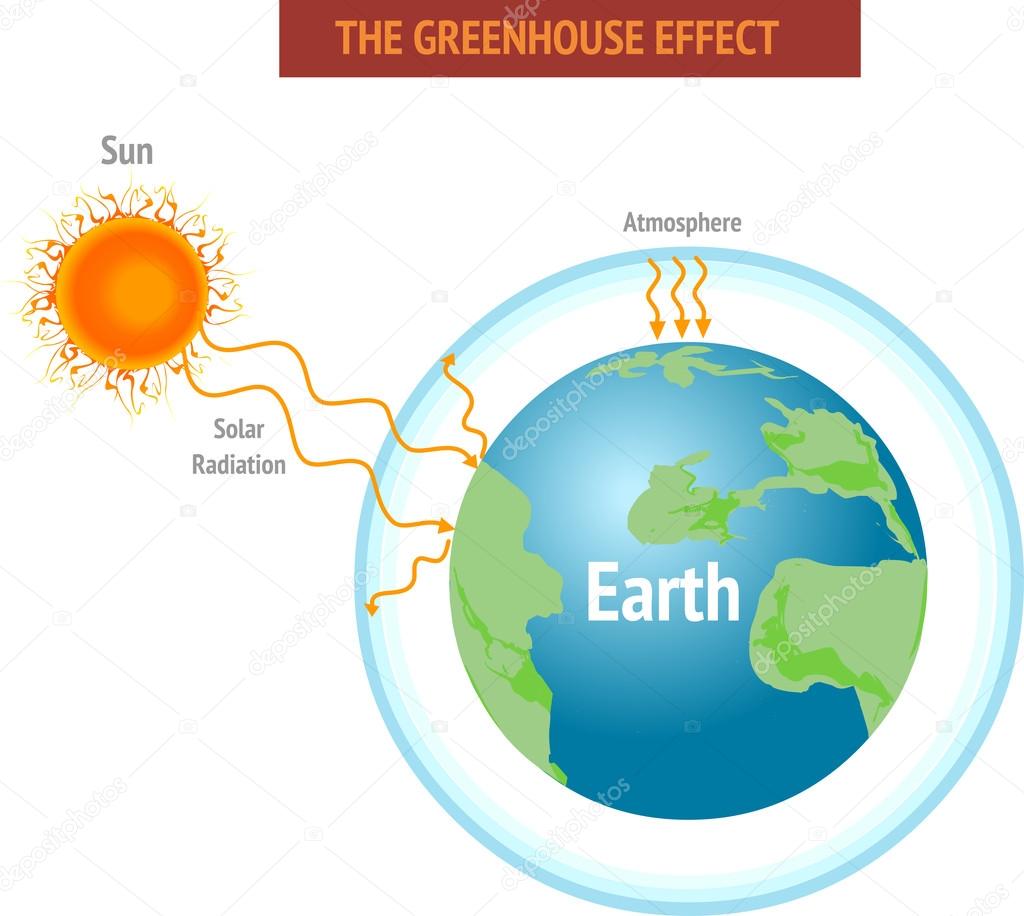
The natural greenhouse effect The natural greenhouse effect is a phenomenon caused by gases naturally present in the atmosphere that affect the behaviour of the heat energy radiated by the sun In simple terms, sunlight (shortwave radiation) passes through the atmosphere, and is absorbed by Earth's surfaceGlobal warming or climate change is the rising of the earth's average temperature day by day caused by the presence of different gases along with carbon dioxide at high levels in the earth's atmosphere The greenhouse effect is essential for sustaining life on Earth The intensity of the warming effect depends on the concentration of the
Greenhouse Effect Experiment hydro Power Smart For Schools
Natural greenhouse effect images
Natural greenhouse effect images- Yes, by increasing the abundance of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, human activities are amplifying Earth's natural greenhouse effect Virtually all climate scientists agree that this increase in heattrapping gases is the main reason for the 18°F (10°C) rise in global average temperature since the late nineteenth centuryWhat is the Natural Greenhouse Effect?




Which Is It Global Warming Global Climate Change Ppt Download
Find Greenhouse Effect Illustration Infographic Natural Process stock images in HD and millions of other royaltyfree stock photos, illustrations and vectors in the collection Thousands of new, highquality pictures added every day As already mentioned in the previous paragraphs, the greenhouse effect is a natural phenomenon, provoked by a mixture of gases that are present in the atmosphere (and defined greenhouse gases) without which there would not be any life on the Earth In the last century, however, the intense human production activities led to an increase Greenhouse gases are gases that can trap heat They get their name from greenhouses A greenhouse is full of windows that let in sunlight That sunlight creates warmth The big trick of a greenhouse is that it doesn't let that warmth escape That's exactly how greenhouse gases act They let
The greenhouse effect is a natural process responsible for keeping the earth at the temperature needed to sustain life Acting just like the glass walls of a greenhouse, gases like carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide trap the sun's heat in the atmosphere and prevent itOn Earth, human activities are changing the natural greenhouse Over the last century the burning of fossil fuels like coal and oil has increased the concentration of atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO 2)This happens because the coal or oil burning process combines carbon with oxygen in the air to make CO 2To a lesser extent, the clearing of land for agriculture, industry, and other humanMain Greenhouse Gases Multiple gases contribute to the greenhouse effect that sets Earth's temperature over geologic time Small changes in the atmospheric concentration of these gases can lead to changes in temperature that make the difference between ice ages when mastodons roamed the Earth, and the sweltering heat in which the dinosaurs lived
This natural greenhouse effect is what keeps the Earth's climate livable Without it, the Earth's surface would be an average of about 60Greenhouse gas emissions increased 70 percent between 1970 and 04 Emissions of carbon dioxide, the most important greenhouse gas, rose by about 80 percent during that time The amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere today farCarbon dioxide (CO 2), which causes 9–26 percent;




Global Warming Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Greenhouse Effect Climate Change Lesson




Greenhouse Effect What It Is How It Occurs And Consequences Iberdrola
The Earth's natural greenhouse effect and account for about 90% of the total heatretaining capacity of the atmosphere Greenhouse gases can also reabsorb solar radiation reflected or reemitted from Earth's surface, trapping the heat in our atmosphere instead of letting it escape to space The Greenhouse Effect is a natural process essentialAnd ozone, which causes 3–7 percentThe issue is how the strength of the greenhouse effect changes when humanThe greenhouse effect is the process by which radiation from a planet's atmosphere warms the planet's surface to a temperature above what it would be without this atmosphere Radiatively active gases (ie, greenhouse gases) in a planet's atmosphere radiate energy in all directionsPart of this radiation is directed towards the surface, thus warming it




The Greenhouse Effect Climate Matters




What Is An Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Universe Today
The 'greenhouse effect' is the warming of climate that results when the atmosphere traps heat radiating from Earth toward space Certain gases in the atmosphere resemble glass in a greenhouse, allowing sunlight to pass into the 'greenhouse,' but blocking Earth's heat from escaping into space The gases that contribute to the greenhouse effect As of 12, the warming effect of longlived greenhouse gases in Earth's atmosphere had increased by approximately 47% compared to 1990 Relative to preindustrial times, today's atmosphere absorbs an extra 3 watts of energy per square meterGreenhouse effect, a warming of Earth's surface and troposphere (the lowest layer of the atmosphere) caused by the presence of water vapour, carbon dioxide, methane, and certain other gases in the air Of those gases, known as greenhouse gases, water vapour has the largest effect The origins of the term greenhouse effect are unclear French mathematician Joseph Fourier is



Too Much Of A Good Thing




Climate Processes Marian Koshland Science Museum
The greenhouse effect happens when certain gases, which are known as greenhouse gases, accumulate in Earth's atmosphereGreenhouse gases include carbon dioxide (CO 2), methane (CH 4), nitrous oxide (N 2 O), ozone (O 3), and fluorinated gases Greenhouse gases allow the sun's light to shine onto Earth's surface, and then the gases, such as ozone, trapMethane (CH 4), which causes 4–9 percent; Greenhouse effect is a concern for students due to the fact that they should know about the pros and cons of certain activities that involve heat radiation beyond the atmospheric level Greenhouse gases have reportedly elevated the mortality rate over the past many years




Climate Change Science And Impacts Factsheet Center For Sustainable Systems




The Anthropogenic Greenhouse Effect Anthropogenic Greenhouse Effect The Enhancement Of The Natural Greenhouse Effect Due To Human Activity The Problem Ppt Download
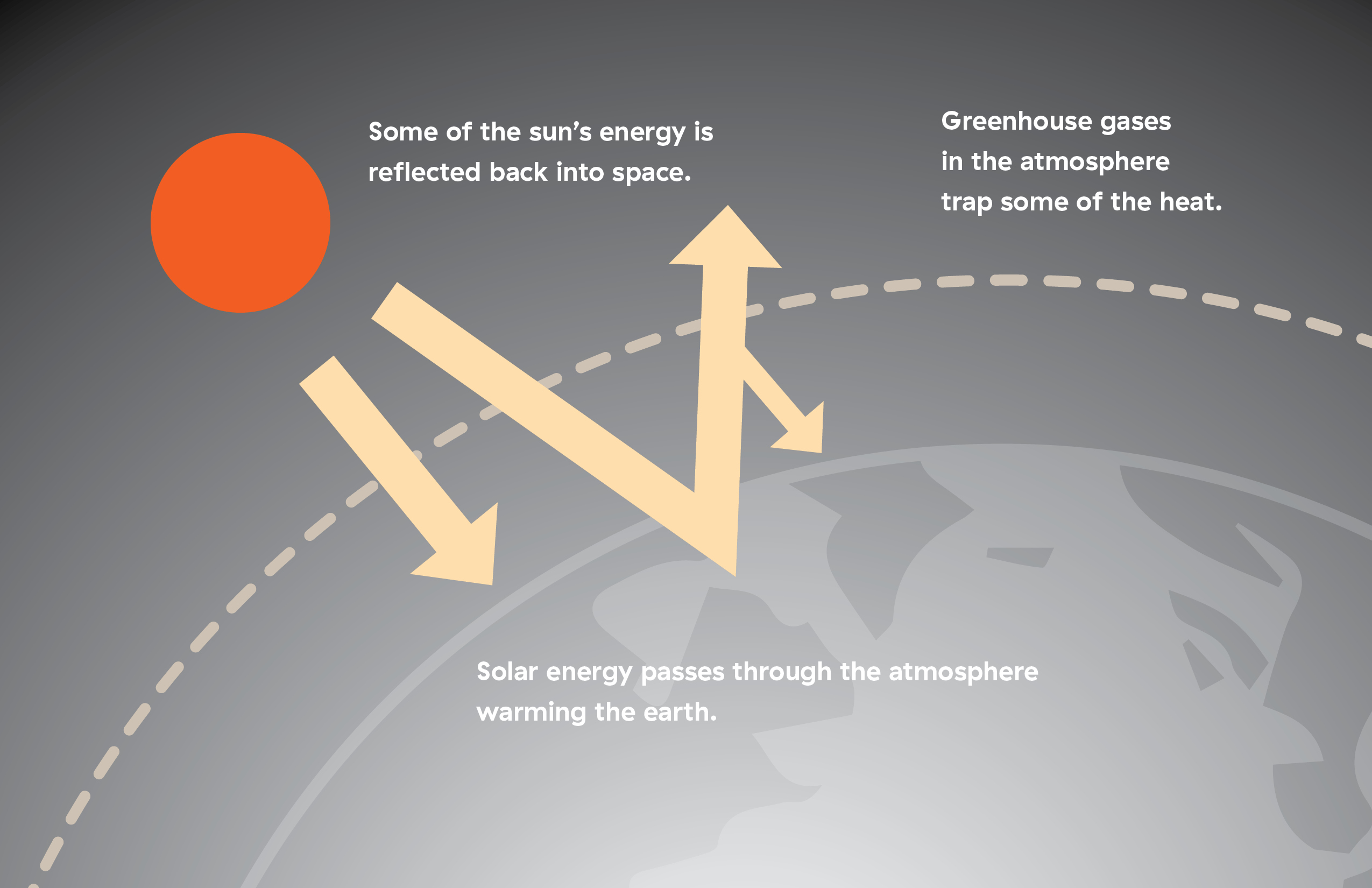
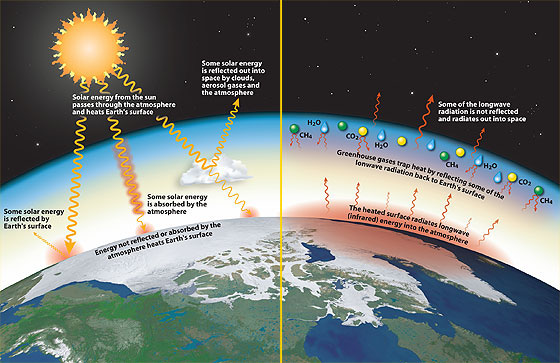
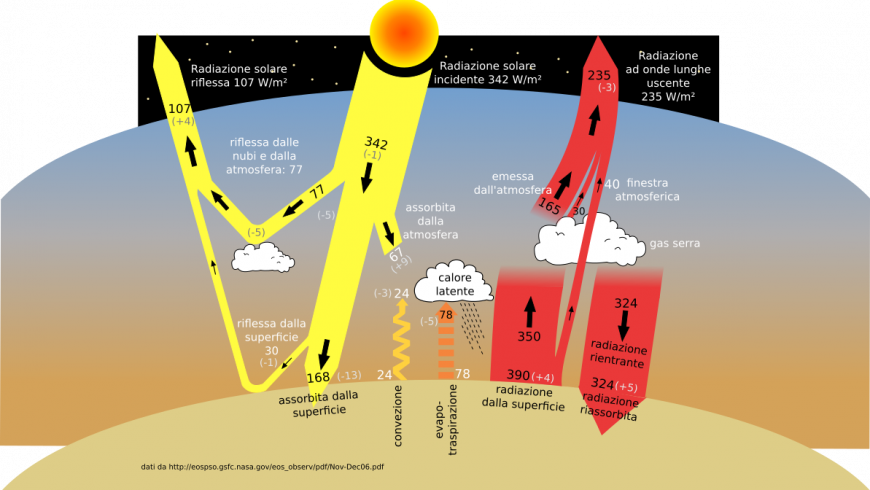
11 Is the greenhouse effect a natural or unnatural process?Planet Earth is billions of years old In its long life, it has undergone temperature shifts from ice ages to periods of global warming Yet overall, itEarth's natural greenhouse effect Earth's temperature begins with the Sun Roughly 30 percent of incoming sunlight is reflected back into space by bright surfaces like clouds and ice Of the remaining 70 percent, most is absorbed by the land and ocean, and the rest is absorbed by the atmosphere The absorbed solar energy heats our planet




The Greenhouse Effect World101




Natural Greenhouse Effect Human Enhanced Greenhouse Stock Vector Royalty Free
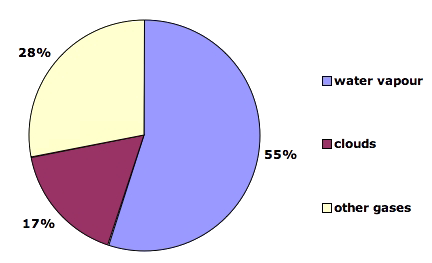
Greenhouse Effect The greenhouse effect The greenhouse effect and climate change Effects of climatic change Resources The greenhouse effect is the retention by Earth ' s atmosphere in the form of heat some of the energy that arrives from the sun as light Certain gases, including carbon dioxide (CO2) and methane (CH4), are transparent to most of the wavelengthsNatural processes and cycles in the Earth system (Figure 1) These include the carbon cycle and greenhouse effect, orbital cycles, ocean currents that distribute warmer and colder water around the globe, and atmosphereocean interactions that moderate temperature Humans are principally affecting the climate systemWater Vapor is naturally occurring and accounts for 36%70% of the greenhouse effect Water vapor is vital to the greenhouse effect which sustains life on earth but, if the atmosphere warms with added carbon dioxide, this can increase the natural amount of water vapor in the air because more water vapor can evaporate into warm air than into



What Gases Are Greenhouse Gases Jean Marc Jancovici



Greenhouse Effect Body Used Water Process Earth Plants Form Energy Gas
If the atmosphere works too well as a greenhouse, each day gets a little warmer and a little warmer We may not be able to measure this effect from day to day or even year to year But over tens of years, a few degrees of warming starts causing changes For example, ice melts in the North and South Pole regions12 How are the greenhouse gases and the glass walls of a greenhouse the same?Atmosphere & Greenhouse Gases The natural greenhouse effect is necessary for the temperature of earth to support current life systems The enhanced greenhouse effect caused by a greater buildup of carbon dioxide and methane (and other greenhouse gases) leads to less radiated heat leaving the atmosphere, resulting in warmer global temperatures




Globalchange Gov Think Of Greenhouse Gases As A Blanket That Absorbs Heat To Keep Our Planet Warm Learn About How Our Activities Are Changing This Natural Greenhouse Effect And What That




Natural Greenhouse Effect Human Enhanced Greenhouse Stock Vector Royalty Free
The greenhouse effect is a natural phenomenon and is beneficial for us Certain gases in the atmosphere retain part of the thermal radiation emitted by the Earth's surface after being heated by the sun, this maintains the planet's temperature at a level suitable for the development of life Human action, however, has increased the presence of Figure nca3 3411 (left) A stylized representation of the natural greenhouse effect Most of the sun's radiation reaches the Earth's surface Naturally occurring heattrapping gases, including water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide, do not absorb the short wave energy from the sun but do absorb the longwave energy reradiated from the Earth, keeping theOn Earth, the major greenhouse gases are water vapor, which causes about 36–70 percent of the greenhouse effect (not including clouds);




Greenhouse Gas Effect Stock Image C033 5439 Science Photo Library



Carbon Connections 1 3 Carbon Forcing
,002 greenhouse effect stock photos, vectors, and illustrations are available royaltyfree See greenhouse effect stock video clips of 1 greenhouse effect diagram commercial spraying water on plants greenhouse gas effect global warming posters sun earth diagram energy poster global warming global warming solutions sun radiating to a plantThe Greenhouse Effect The greenhouse effect is a naturally occurring phenomenon in which the specific gases in the atmosphere of the Earth trap heat from the sun (see The Greenhouse Effect Diagram attachment) Typically, our atmosphere absorbs just the right amount of heat so that living things can surviveNatural greenhouse gases include water vapour, carbon dioxide, methane, nitrogen protoxide and ozone Some human activities contribute to the increase in the concentration of these gases in the atmosphere and, furthermore, they free other greenhouse gases that are exclusively anthropogenic in the air Let us now examine the characteristics of the principal gases which




Greenhouse Gases And The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Video Lesson Transcript Study Com




What Is The Greenhouse Effect
14 What is the opinion of most scientists about the greenhouse effect 15 Draw 2 pictures showing how the greenhouse effect and global warming workThe Earth's greenhouse effect is a natural consequence of the chemical makeup of its atmosphere If it were not for the greenhouse effect, life as we know it could not exist on Earth it would be too cold Our atmosphere is made mostly of nitrogen and oxygen, but also contains several other gases These include13 Why is the increase in greenhouse gases a problem?




The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Geographycasestudy Com




Natural And Unnatural Greenhouse Effect Ppt Download
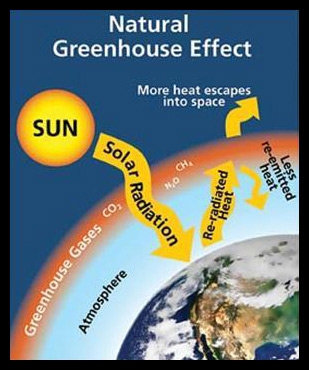
Greenhouse Effects BIBLIOGRAPHY The natural greenhouse effect was first described by Joseph Fourier (1768 – 10) in 17 Solar energy reaches the earth in the entire spectrum The earth reemits this energy as infrared radiationGreenhouse gases in the atmosphere, such as water vapor and carbon dioxide, absorb outgoing infrared radiation and reemit it in any direction The greenhouse effect occurs when the sun's rays reach the Earth's atmosphere and the majority of the radiation bounces back out into space When this happens, a small portion is absorbed by chemicals in our atmosphere These are known as greenhouse gases By looking at air bubbles from hundreds of thousands of years ago until today The greenhouse effect is the way in which heat is trapped close to Earth's surface by "greenhouse gases" These heattrapping gases can be thought of as a blanket wrapped around Earth, keeping the planet toastier than it would be without them Greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxides




What Is The Greenhouse Effect
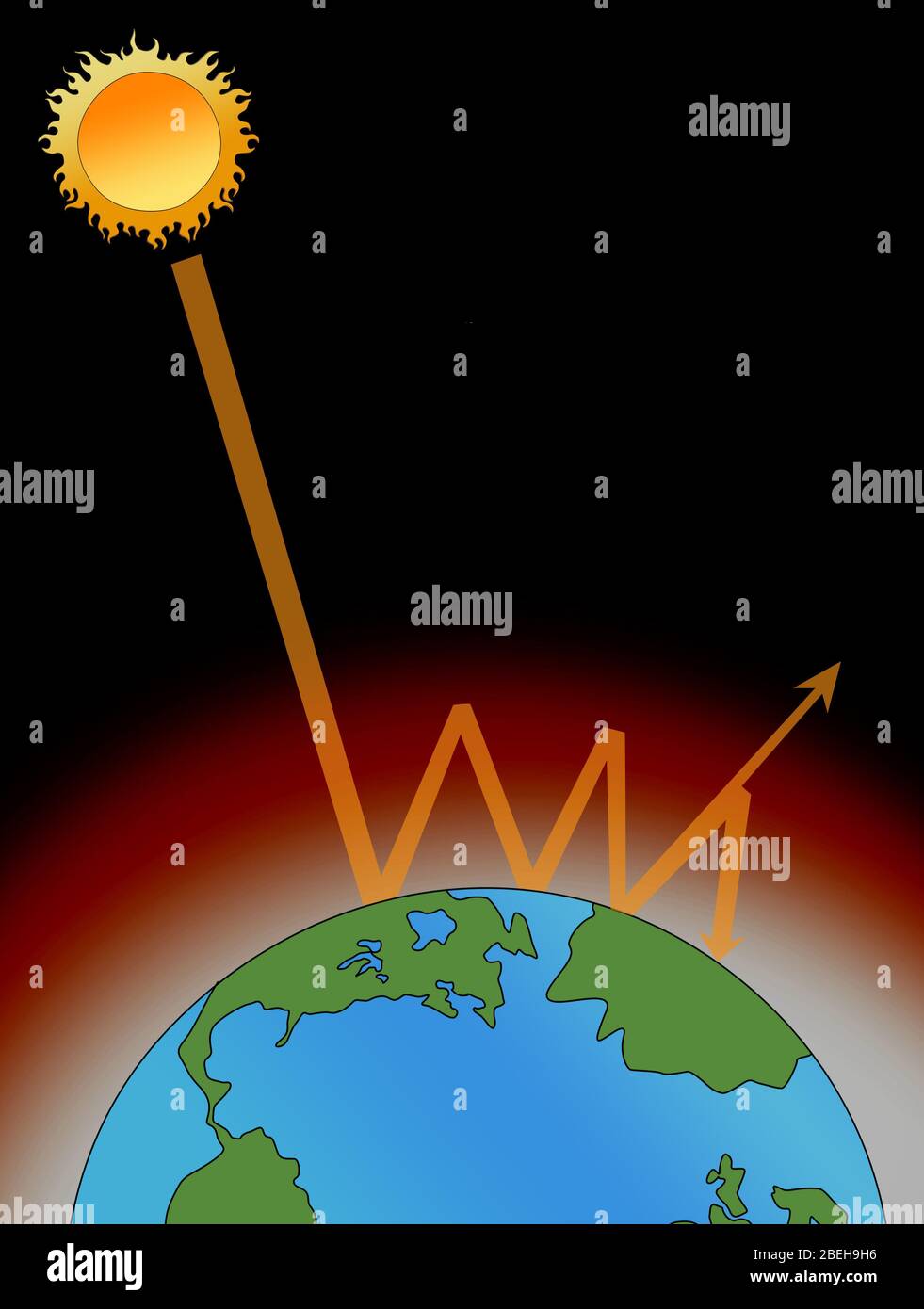



Greenhouse Effect High Resolution Stock Photography And Images Alamy
Both natural processes and humanbased activities The warming effect of trace gas greenhouse gas is enhanced by the effect of water vapour, which also absorbs infrared radiation, leading to an important natural feedback effect between anthropogenic greenhouse gas and water vapour (Figure 111) A certain level of greenhouse gas is The greenhouse effect is a natural process that has maintained Earth's temperature at a habitable level However, human activities — in particular, the burning of fossil fuels — release additional greenhouse gases into the atmosphere These additional gases increase the greenhouse effect, making Earth warmer than usual
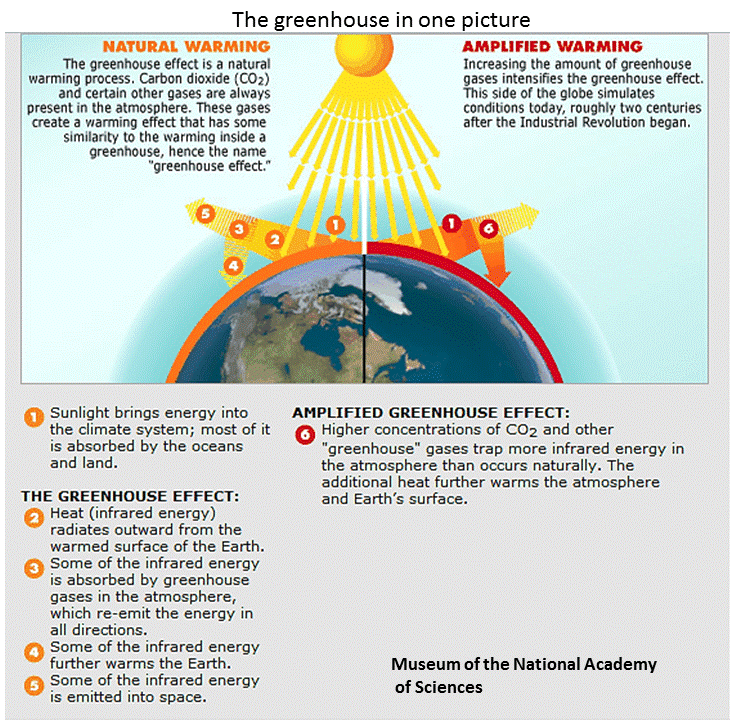



Greenhouse Effect



Climate Science Investigations South Florida Energy The Driver Of Climate




Greenhouse Effect 101 Nrdc



Climate Science Investigations South Florida Energy The Driver Of Climate




Carbon Dioxide Methane Nitrous Oxide And The Greenhouse Effect Conservation In A Changing Climate
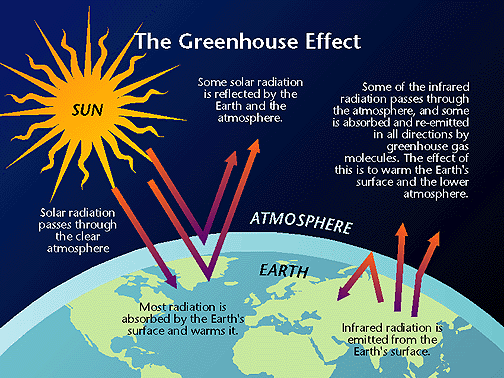



This Is Historical Material Frozen In Time The Web Site Is No Longer Updated And Links To External Web Sites And Some Internal Pages Will Not Work Life As We Know It Is Possible On Earth Because Of A Natural Greenhouse Effect That Keeps Our Planet About 60o
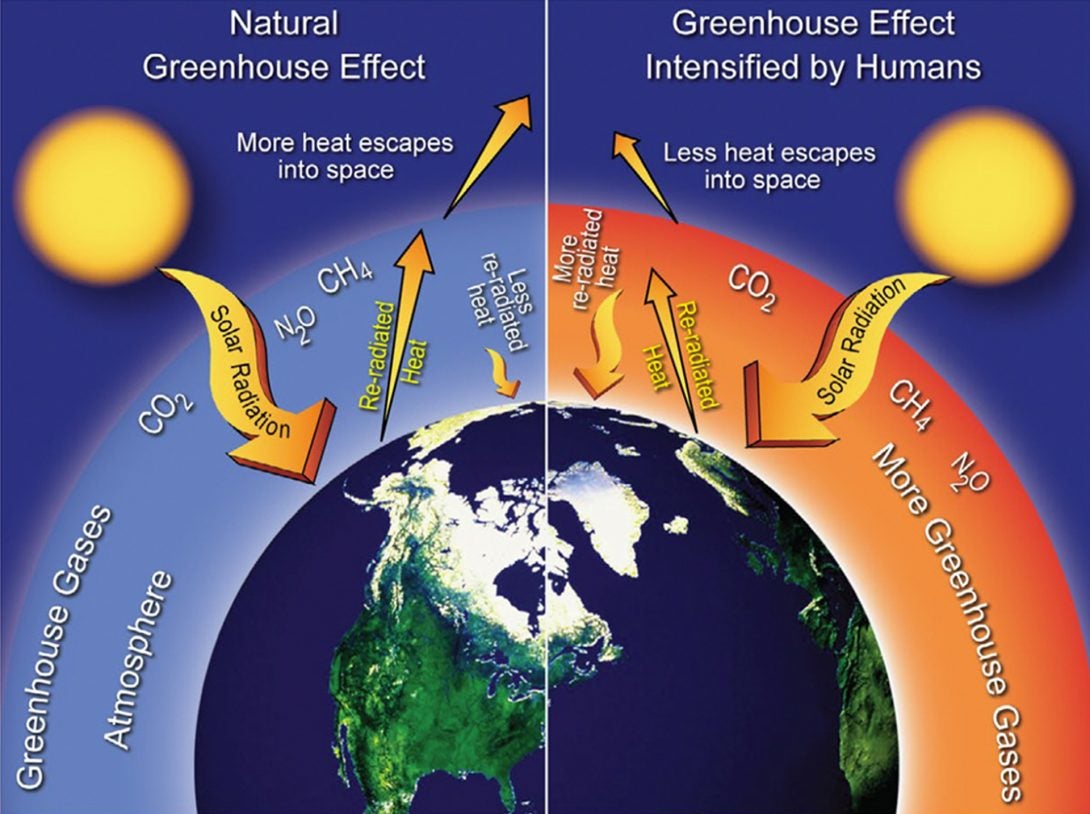



Causes Building Resilience Against Climate Effects University Of Illinois Chicago




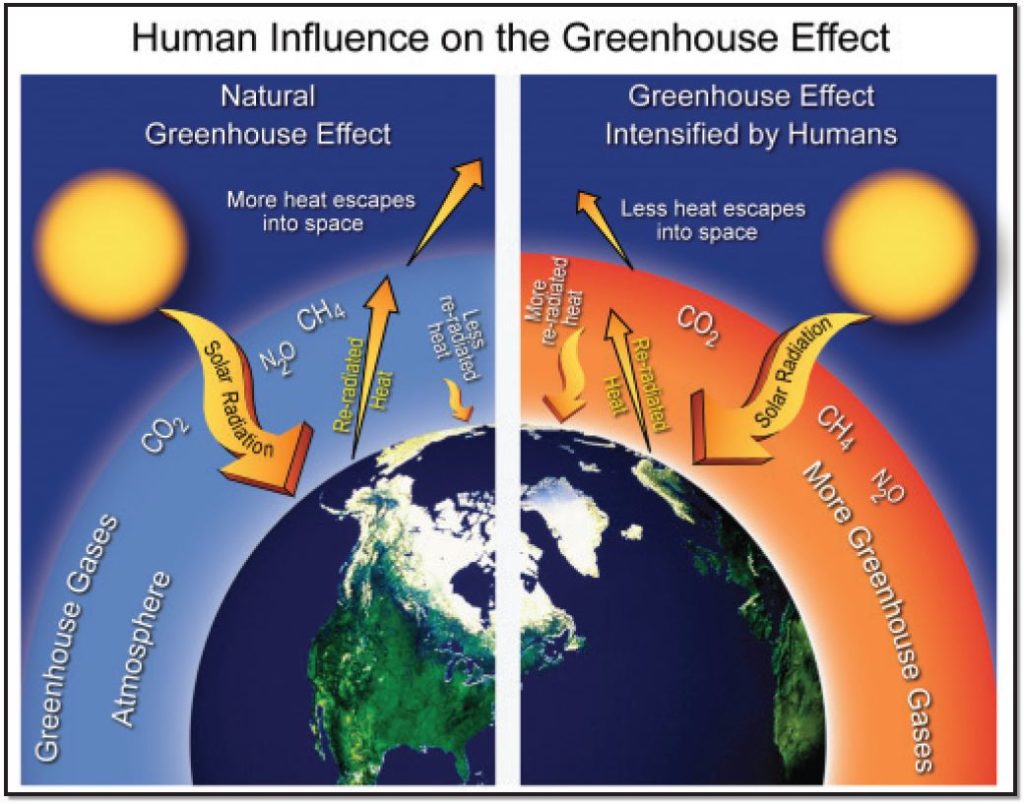
Human Influence On The Greenhouse Effect Globalchange Gov




Greenhouse Effect Experiment hydro Power Smart For Schools




Environment Air Pollution Global Warming Facts Ozone Layer Effects Of Global Warming



Climate Topics Global Weather Climate Center




Carbon Dioxide Capture Ferize Vahabova Greenhouse Effect Naturally Occurring Greenhouse Gases Normally Trap Some Of The Sun S Heat Keeping Ppt Download



The Greenhouse Effect




1 The Greenhouse Effect Natural And Anthropogenic Ppt Video Online Download




Greenhouse Effect Wikipedia




Weatherquestions Com What Is The Greenhouse Effect What Are Greenhouse Gases




Greenhouse Effect 101 Nrdc




Global Energy Balance The Natural Quot Greenhouse Effect Quot Instaar



Greenhouse Gases What Are They What Can We Do To Reduce Emissions
.png)



Greenhouse Effect Energy Education
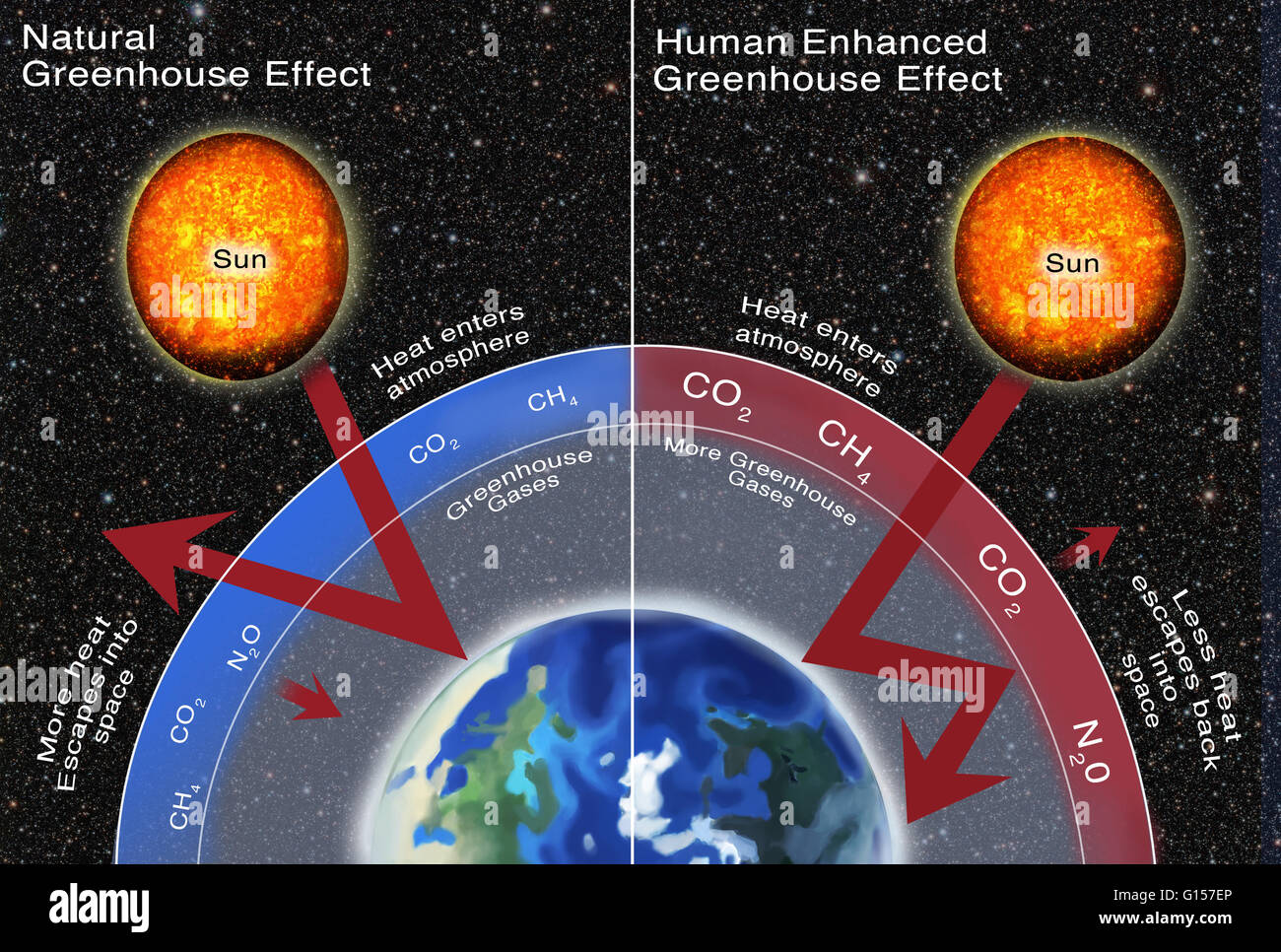



Greenhouse Gas Effect Comparison Illustration Comparing The Natural Greenhouse Gases Emitted To The Human Enhanced Greenhouse Gases Emitted With A Higher Emission Of Greenhouse Gases Shown On The Right More Heat Is




Graphical Illustration Of Natural And Anthropogenic Greenhouse Effects Download Scientific Diagram



1 659 Greenhouse Effect Vector Images Greenhouse Effect Illustrations Depositphotos




Natural Greenhouse Effect Stock Illustration




Greenhouse Effect Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock



3




Representation Of The Natural Greenhouse Gas Effect Higher Levels Of Download Scientific Diagram



Greenhouse Effect And Anthropogenic Warming Mrgeogwagg
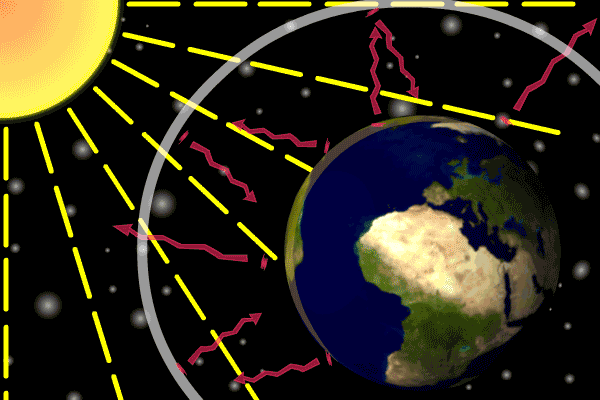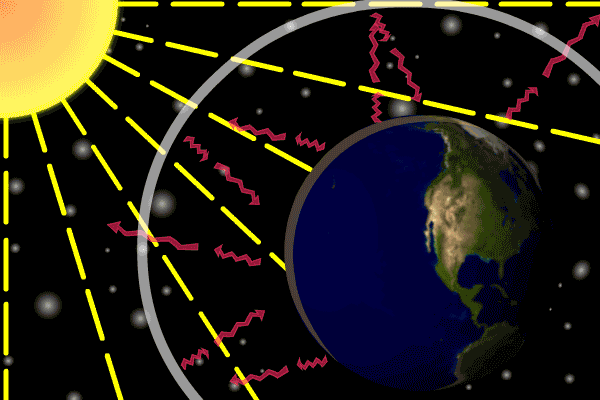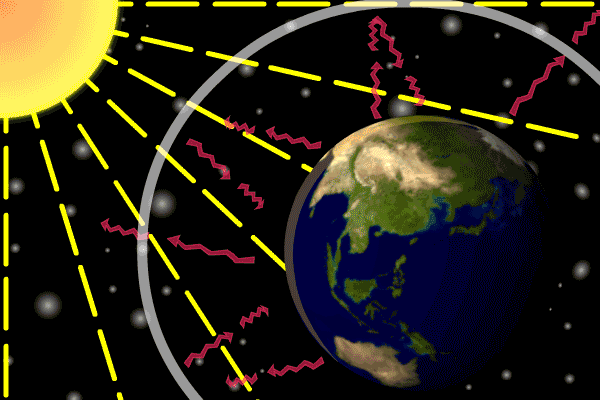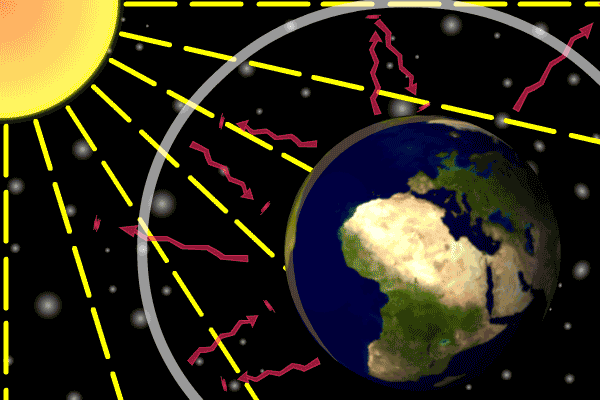



1 The Natural Greenhouse Effect
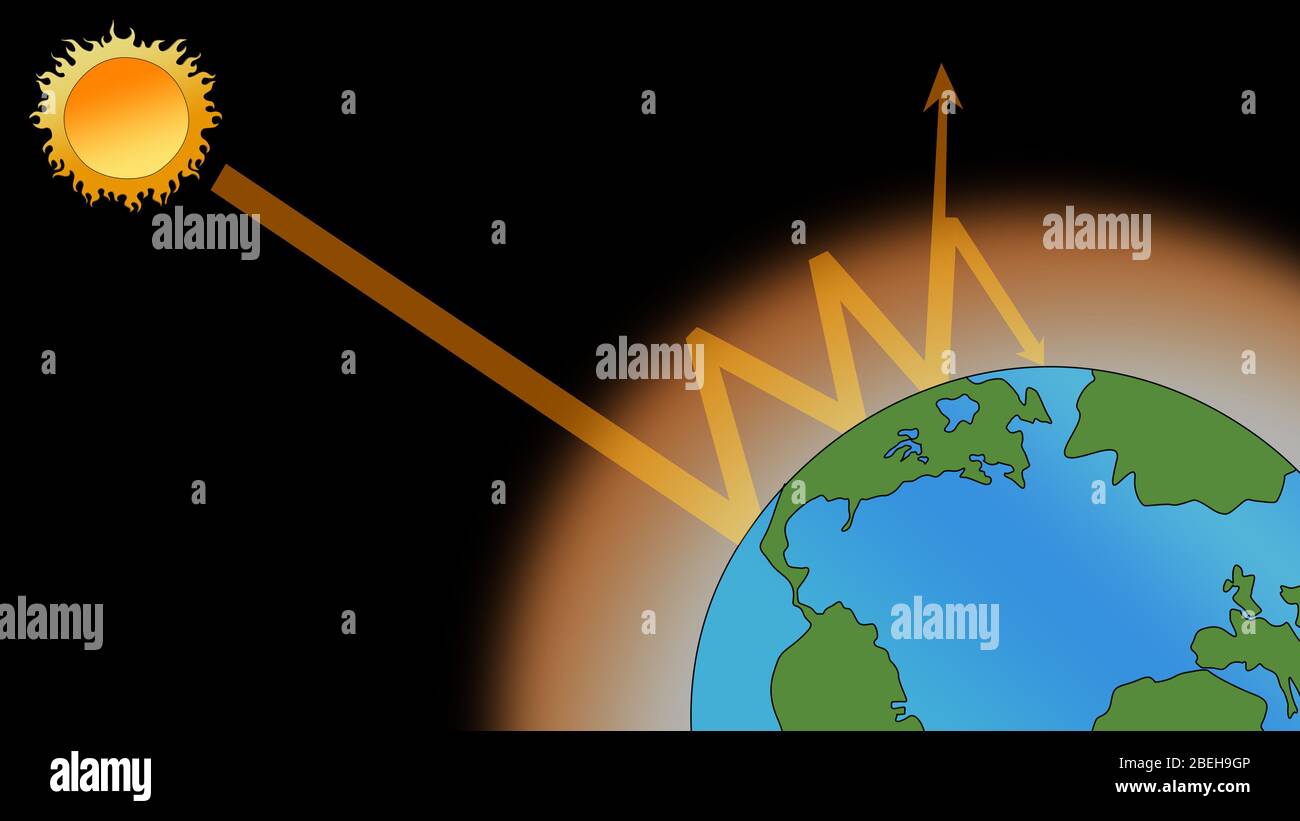



Greenhouse Effect High Resolution Stock Photography And Images Alamy



How Greenhouse Gases Influence Climate The Weather Gamut




Greenhouse Effect Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock




Greenhouse Effect Effect En Green House Glogster Edu Interactive Multimedia Posters
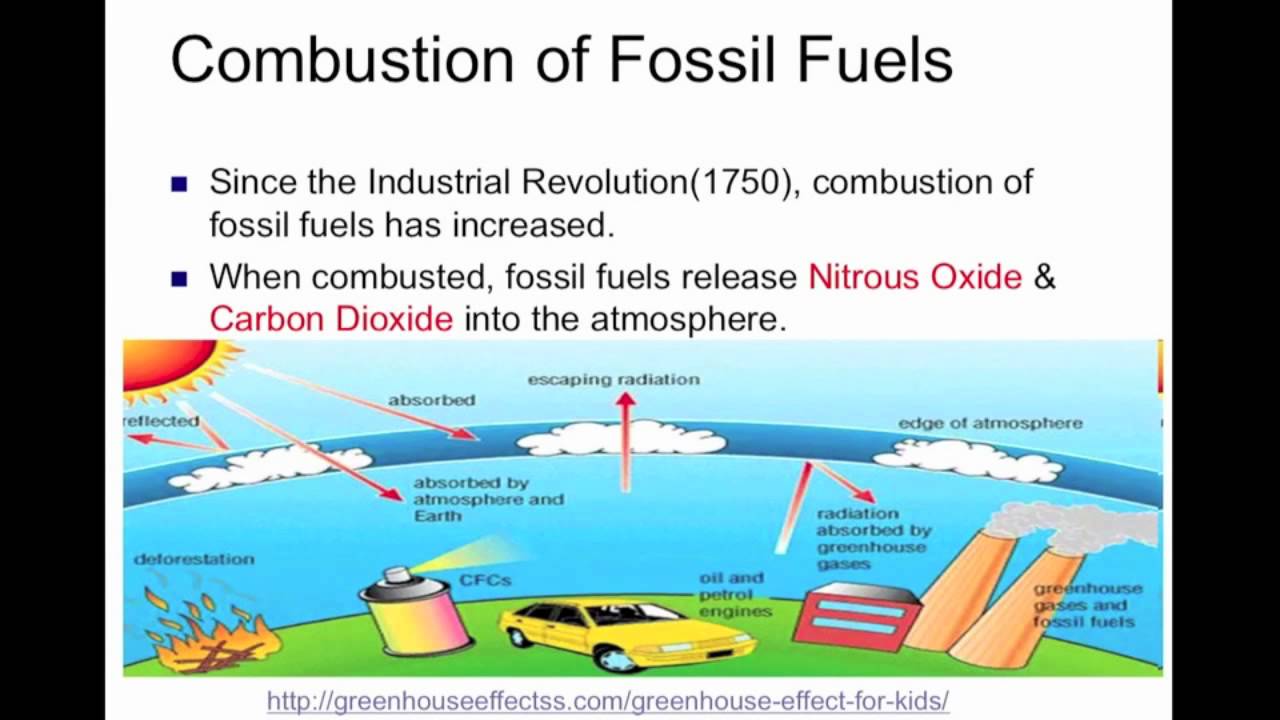



Sts The Natural Greenhouse Effect Vs The Anthropogenic Greenhouse Effect By Sean Andrew Youtube




How Does Earth S Greenhouse Effect Work Saving Earth Encyclopedia Britannica




Greenhouse Effect Department Of Agriculture Water And The Environment



Climate Science Climate Resource Exchange



1



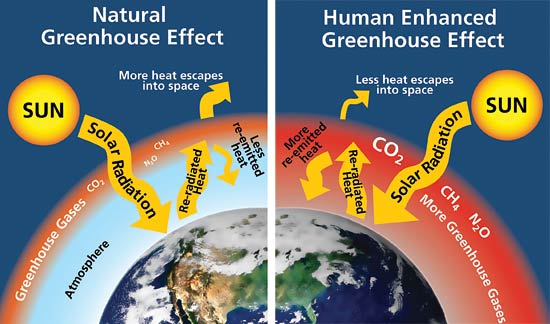
A Natural Greenhouse Effect B Human Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Download Scientific Diagram
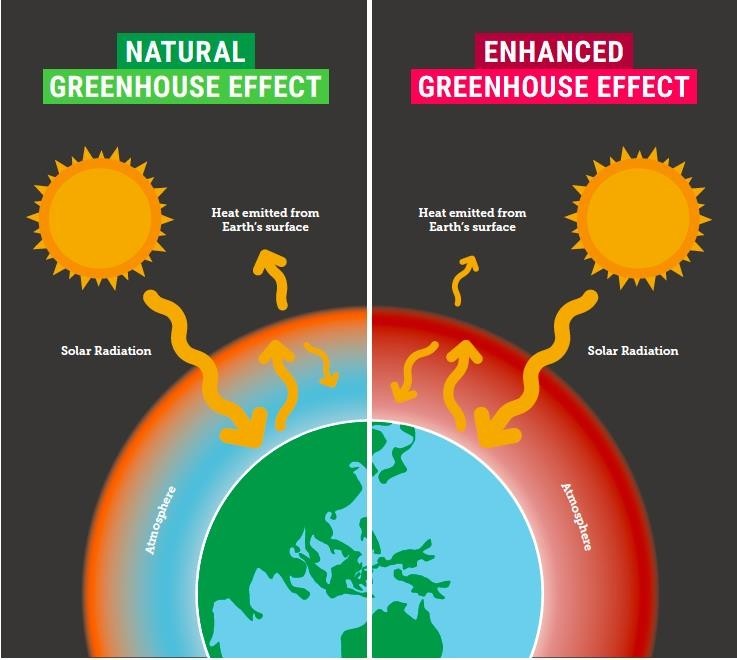



The Greenhouse Effect Sustainable Energy Network Solutions




The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Curious




An Idealized Model Of The Natural Greenhouse Effect Source Ipcc Wg1 Download Scientific Diagram



Ozone Layer
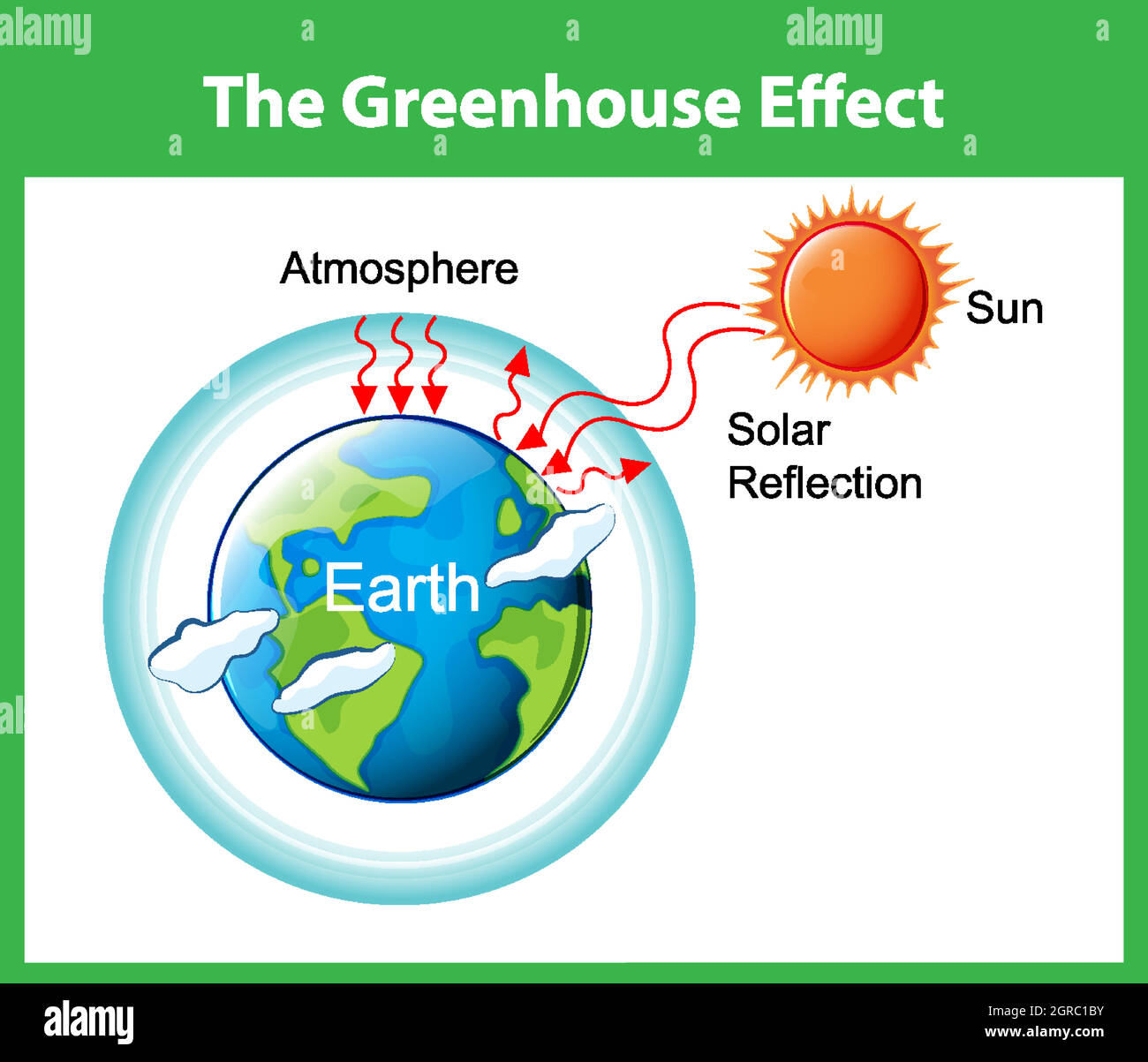



Greenhouse Effect Graphic High Resolution Stock Photography And Images Alamy




Greenhouse Effect Nurturing The Myriad Greens




Which Is It Global Warming Global Climate Change Ppt Download




5 Notorious Greenhouse Gases Britannica



Earth Environment Greenhouse Effect Natural Greenhouse Effect Image Visual Dictionary Online




The Greenhouse Effect Niwa



2



English Comprehension Green House Worksheets 6th Grade Cbse



13 4 Pollution Introduction To Human Geography




The Greenhouse Effect Is A Natural Process Necessary For Sustaining Life On Earth Is A Natural Process Necessary For Sustaining Life On Earth Is Produced Ppt Download




Greenhouse Effect Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock




The Perks Of Greenhouse Effect Top 5 Advantages Of Greenhouse Gases By Ameelia Black Medium




The Greenhouse Effect British Geological Survey




Greenhouse Effect Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock




The Greenhouse Effect World101




A Natural Greenhouse Effect B Human Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Download Scientific Diagram




What Do You Need To Know About Thermal Energy The Physics Cafe




Federation Of Maori Authorities Kia Ora Whanau What Are Greenhouse Gases Or Ghg For Short Earth S Atmosphere Is A Mix Of Gases Water Vapour And Particles That Constantly Mix And Mingle




1 659 Greenhouse Effect Vector Images Greenhouse Effect Illustrations Depositphotos




Greenhouse Effect Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock




1 1 Science Of The Natural Greenhouse Effect A Greener Future
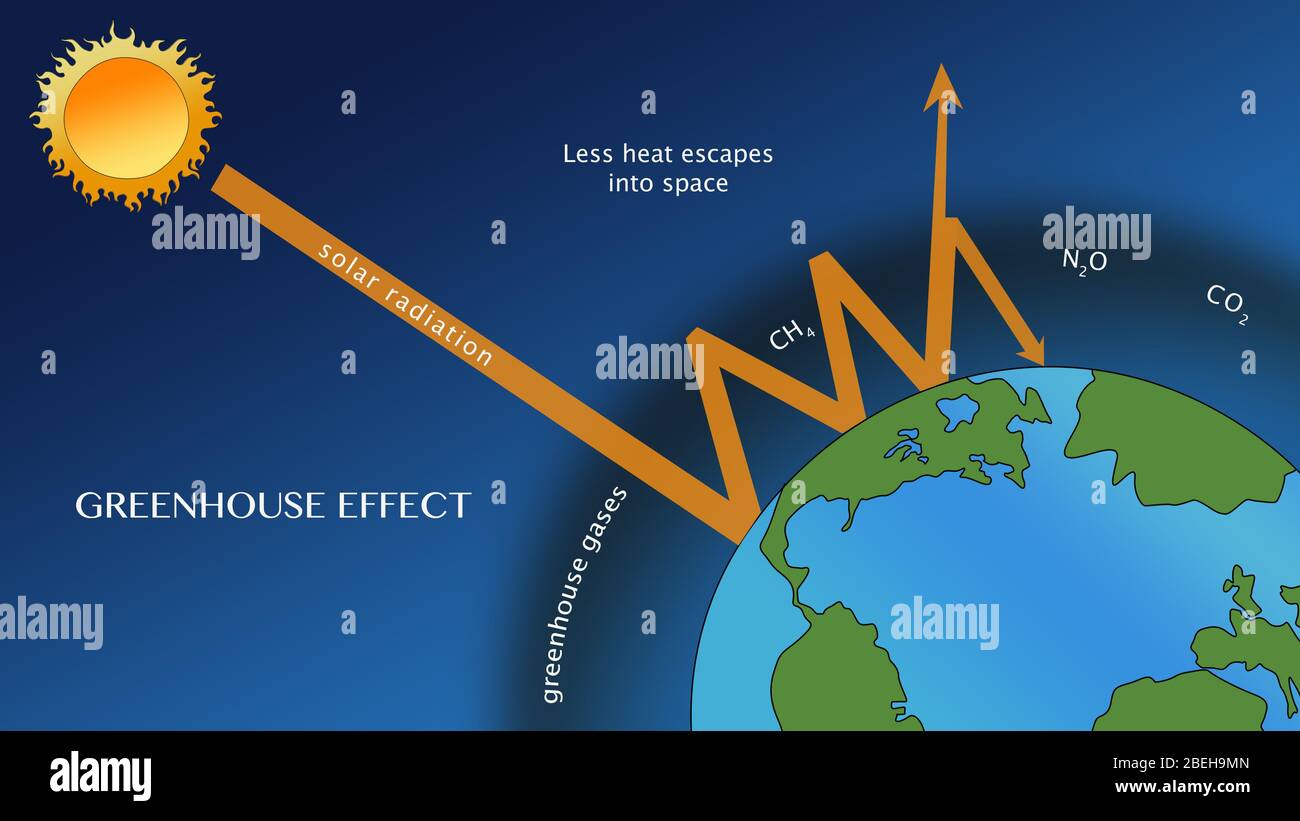



Human Enhanced Greenhouse Effect High Resolution Stock Photography And Images Alamy



1 The Natural Greenhouse Effect




12 445 Greenhouse Effect Stock Photos And Images 123rf




12 445 Greenhouse Effect Stock Photos And Images 123rf




What Is Climate Change Climate Assembly




The Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Brian Williams
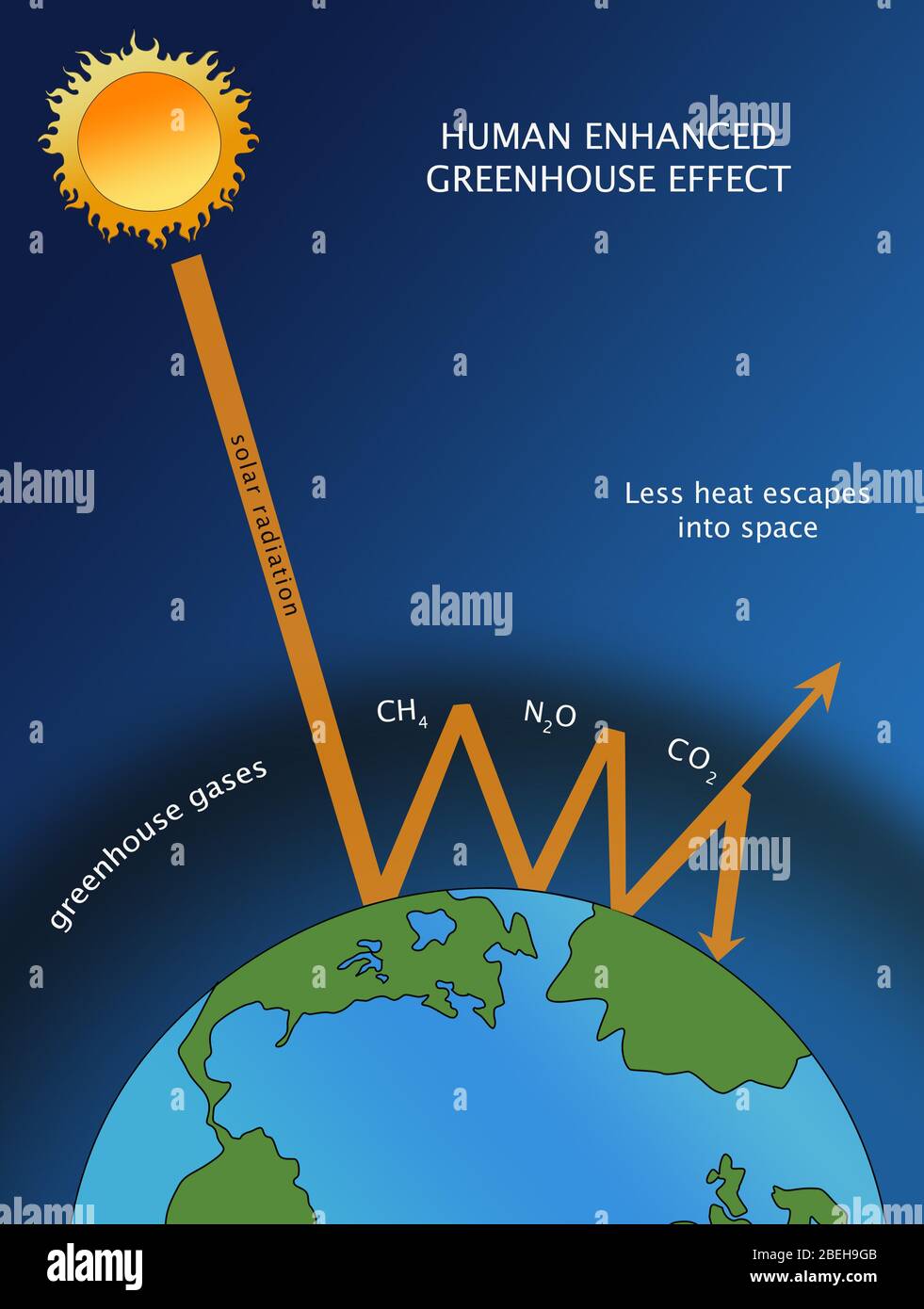



Human Enhanced Greenhouse Effect High Resolution Stock Photography And Images Alamy




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa



Mr G S Environmental Systems 6 1 1 The Natural Greenhouse Effect




What Is Natural Greenhouse Effect Facts And Climate Change Average Temperature Of Planets And Earths Temperature Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gases Greenhouse
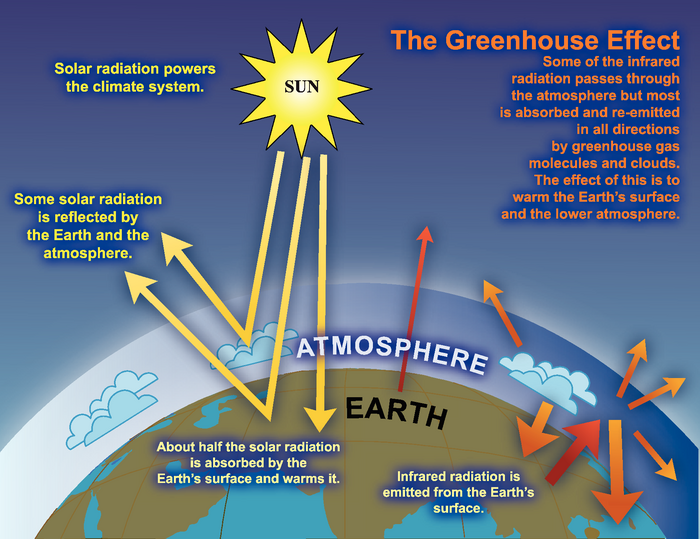



What Is The Greenhouse Effect Niwa




Graphical Illustration Of Natural And Anthropogenic Greenhouse Effects Download Scientific Diagram



3
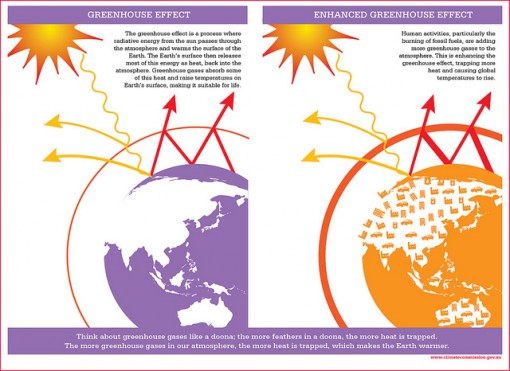



What Is The Greenhouse Effect Conserve Energy Future




30 106 Greenhouse Gas Stock Photos Pictures Royalty Free Images Istock
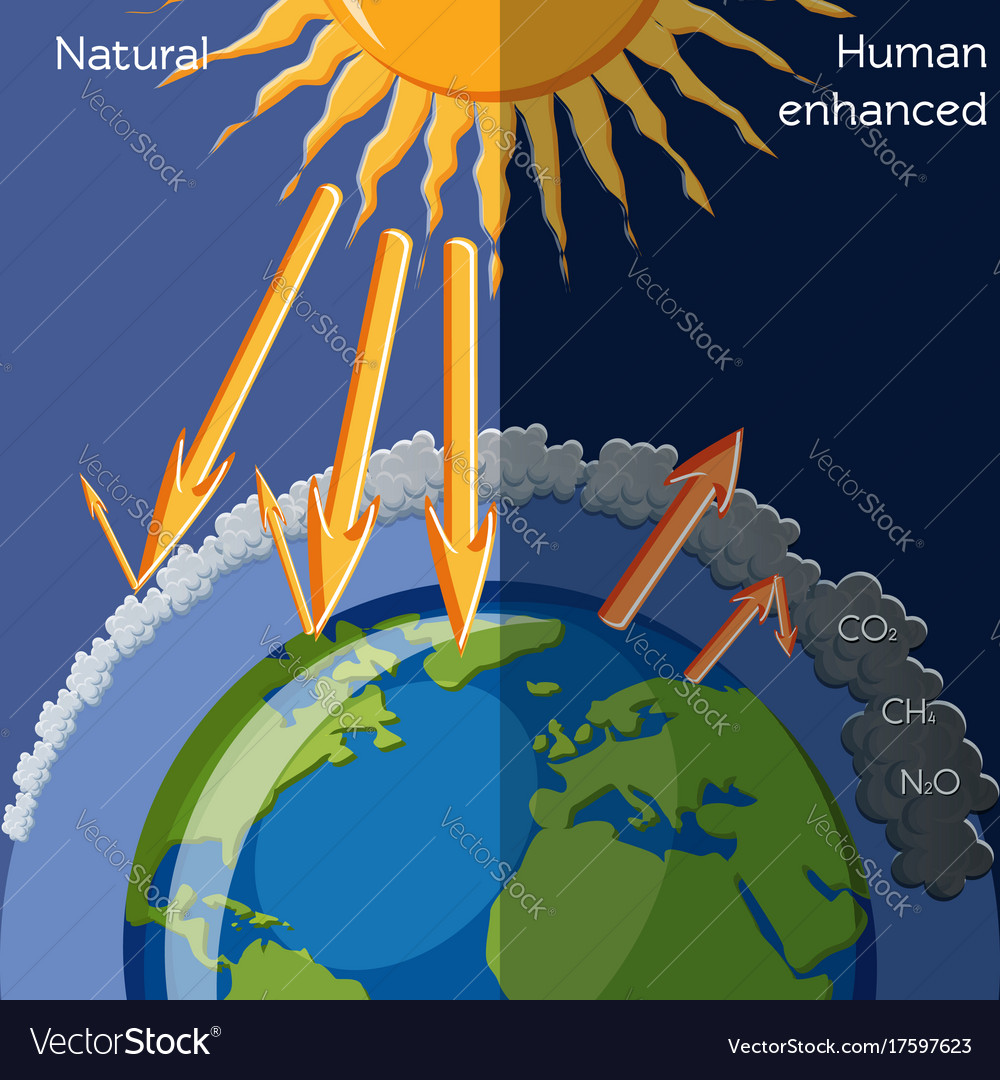



Natural And Human Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Vector Image




Climate Change Background Georgian Bay Biosphere
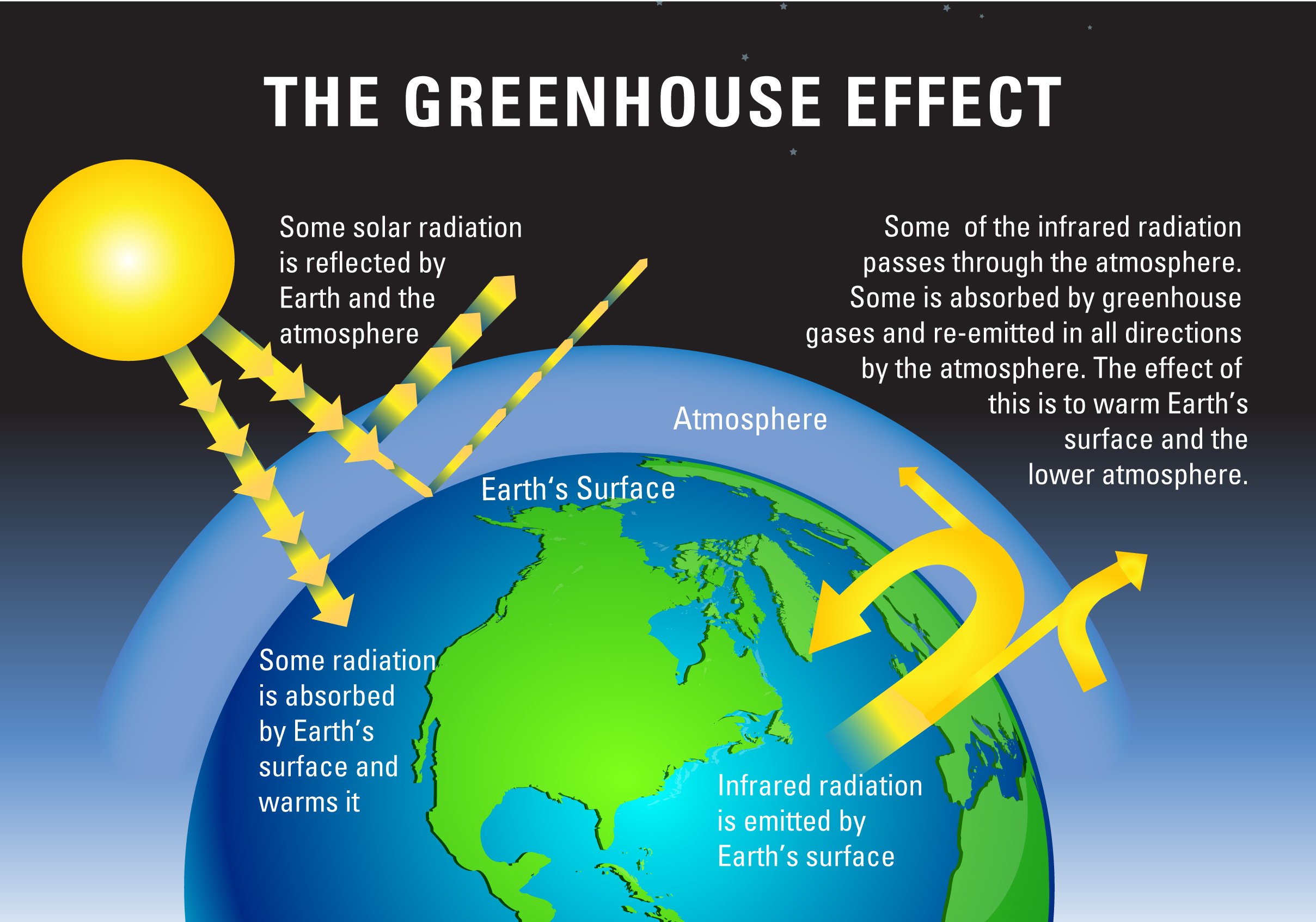



Greenhouse Gases Earth Journalism Network



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿